Development Trend of Rigid-Flexible PCB Manufacturing Technology
Due to different types of substrates, the manufacturing process of rigid-flex PCB is different. The main processes that determine its performance are thin wire technology and microporous technology. With the requirements of miniaturization, multi-function and centralized assembly of electronic products, the manufacturing technology of rigid-flexible PCB and embedded flexible PCB of high-density PCB technology has attracted extensive attention.
Rigid-flex PCB manufacturing process:
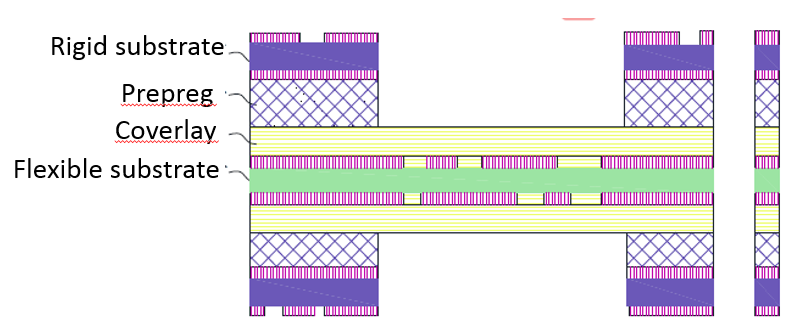
Rigid-Flex PCB, or RFC, is a printed circuit board that combines rigid PCB and flexible PCB, which can form interlayer conduction through PTH.
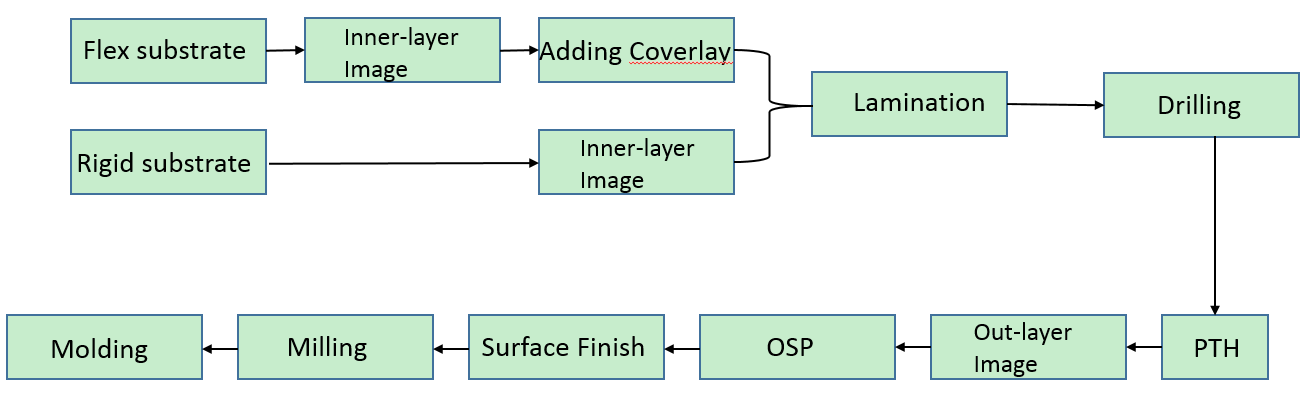
Simple manufacturing process of rigid-flex PCB:
After continuous development and improvement, various new rigid-flexible PCB manufacturing technologies continue to emerge. Among them, the most common and mature manufacturing process is to use rigid FR-4 as the rigid substrate of the rigid-flex PCB outer board, and spray solder ink to protect the circuit pattern of the rigid PCB components. Flexible PCB components use PI film as a flexible core board and cover polyimide or acrylic film. Adhesives use low-flow prepregs, and finally these substrates are laminated together to make rigid-flex PCBs.
The development trend of rigid-flex PCB manufacturing technology:
In the future, rigid-flexible PCBs will develop in the direction of ultra-thin, high-density, and multi-functional, thereby driving the industrial development of corresponding materials, equipment, and processes in upstream industries. With the development of material technology and related manufacturing technologies, flexible PCBs and rigid-flexible PCBs are developing towards interconnection, mainly in the following aspects.
1) Research and develop high-precision processing technology and low dielectric loss materials.
2) Breakthrough in polymer material technology to meet higher temperature range requirements.
3) Very large devices and flexible materials can produce larger and more flexible PCBs.
4) Increase the installation density and expand the embedded components.
5) Hybrid circuit and optical PCB technology.
6) Combined with printed electronics.
To sum up, the manufacturing technology of rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) continues to advance, but some technical problems have also been encountered. However, with the continuous development of electronic product technology, the manufacturing of flexible PCB